The AMD RX 5700 NAVI Series Explained

These are exciting times with not only the Ryzen Zen 2 hitting us, but the new AMD Radeon RX 5700 NAVI graphics cards have also made their way to consumers. Here, AMD has departed from the GCN (Graphics Core Next) architecture in favor of the RDNA architecture, which we’ll have a look at today.

AMD has updated their Adrenalin 2019 software in preparation of the new AMD Radeon RX 5700 (XT) graphics cards. This brings new technology and hopefully better performance vs. power consumption. What this new software entails, we will examine in this article.


The new RDNA architecture used in the new Radeon RX 5700 (XT) graphics cards is built on the same 7 nm graphics chip that we also got acquainted to in our Radeon VII test. The chip itself takes up a mere 251 square millimeters and it brings new GDDR6 VRAM to the table, which differentiates it from the Radeon VII that came equipped with HBM2 VRAM. Additionally, we get support of PCIe Gen. 4.0, which of course is also backwards compatible with Gen. 3.0. However, the new generation brings us double the bandwidth on the PCIe socket. This might not matter so much today, but for future graphics cards this might become a defining factor in order to achieve maximum performance.
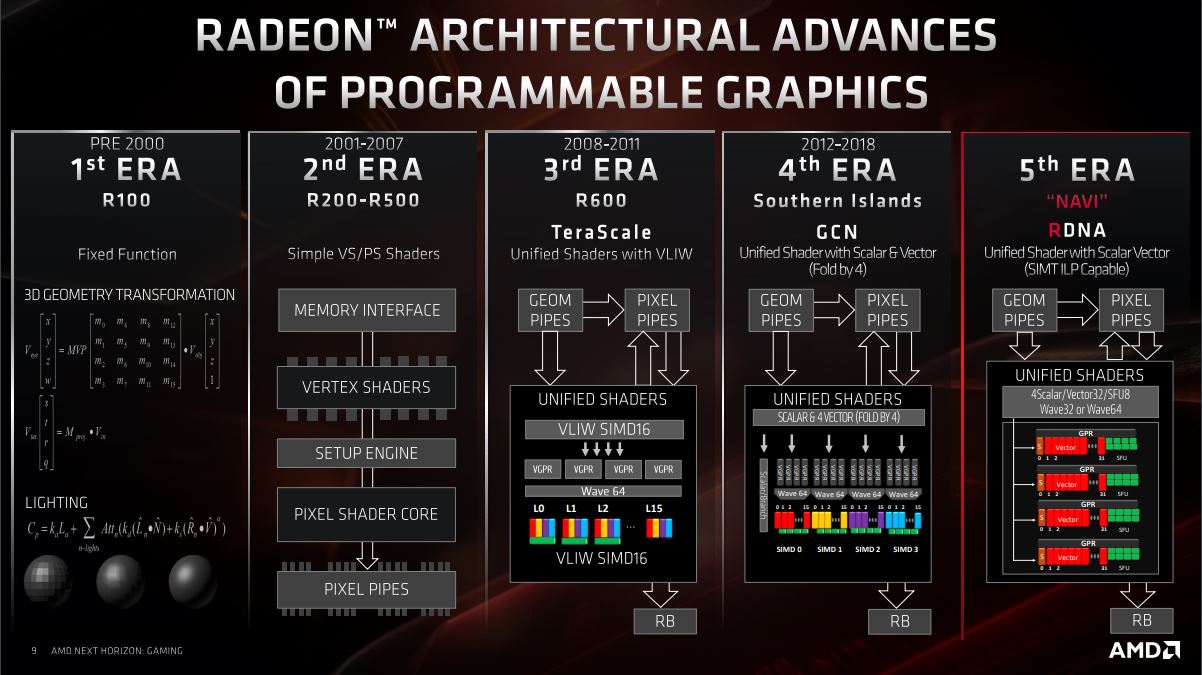
Here, we can see AMD’s development up until today, where we have a fully adaptive graphics chip that can perform a lot of instructions and advanced graphical calculations simultaneously, thus providing users with the best gaming experience or 3D rendering performance available.
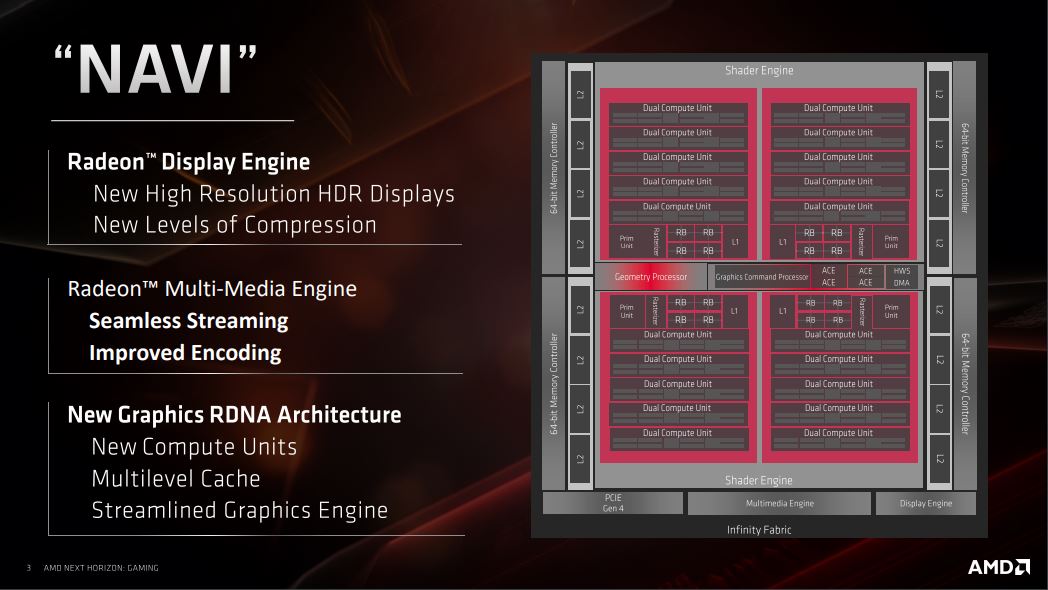
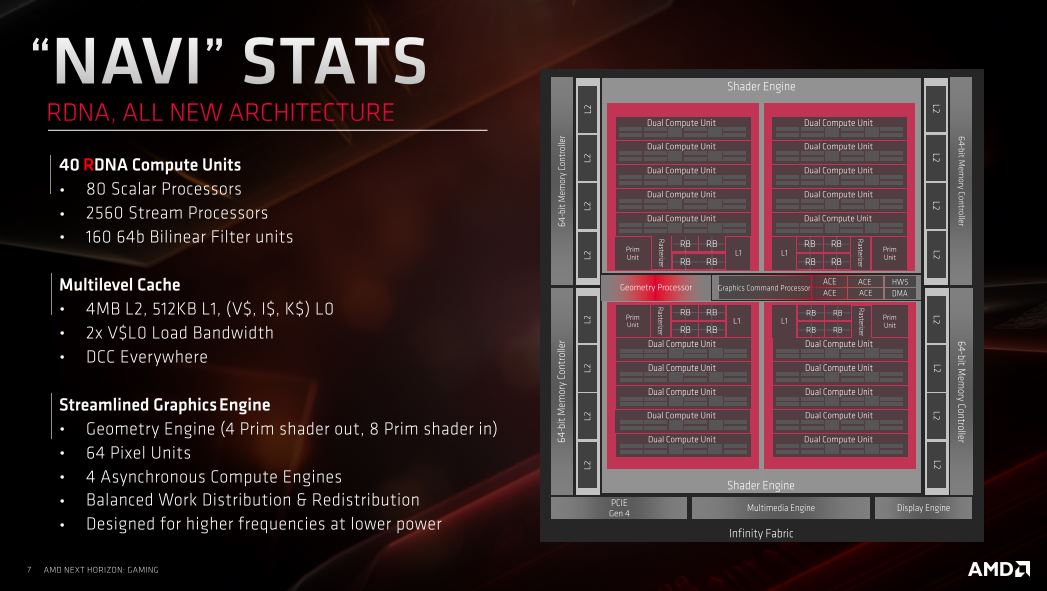
AMD has developed a Dual Compute Unit that means that each compute unit can handle two threads, or instructions if you will, at the same time.

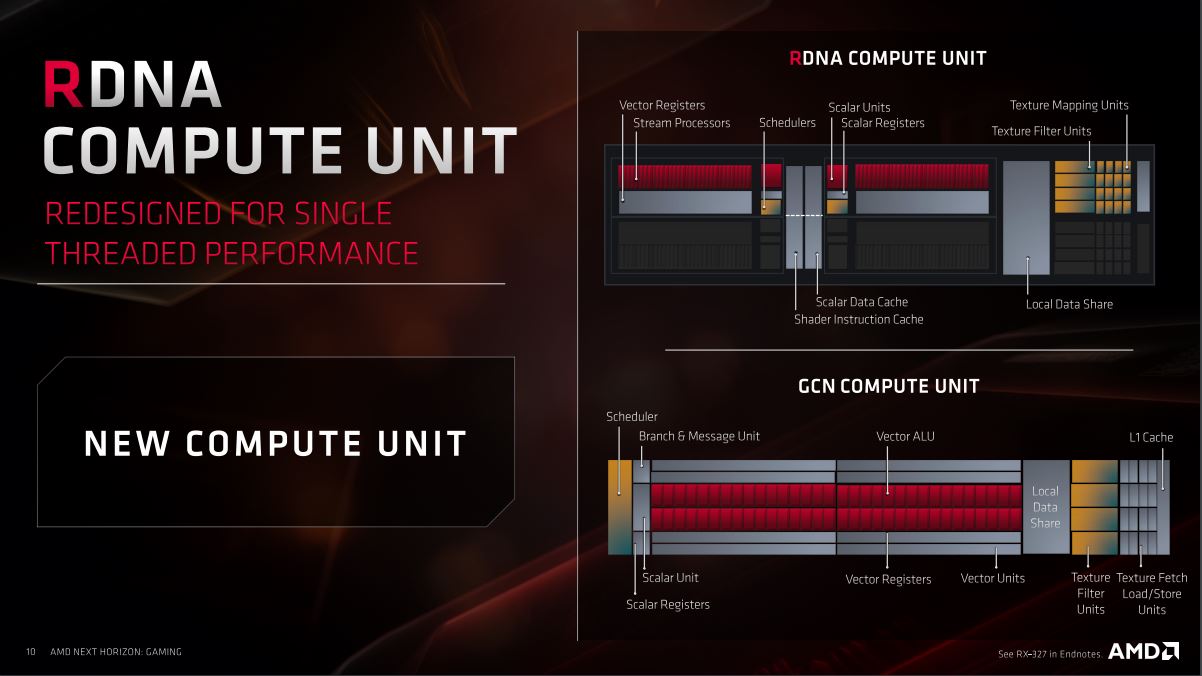
The technology behind consists of the new units being equipped with two Scalar Units and two Schedulers that each has its own cache. This allows for each Compute Unit to handle two instructions at a time, just as single cycle instructions also can be run since the new Compute Units themselves shifts between Wave32 and Wave64 depending on the workload that runs through. This in turn is an efficiency improvement in relation to the power consumption since Wave32 instructions do not activate the Wave64 mode fully. The difference lies with GCN architecture only having a Scheduler, and therefore it could only perform a single instruction at a time.
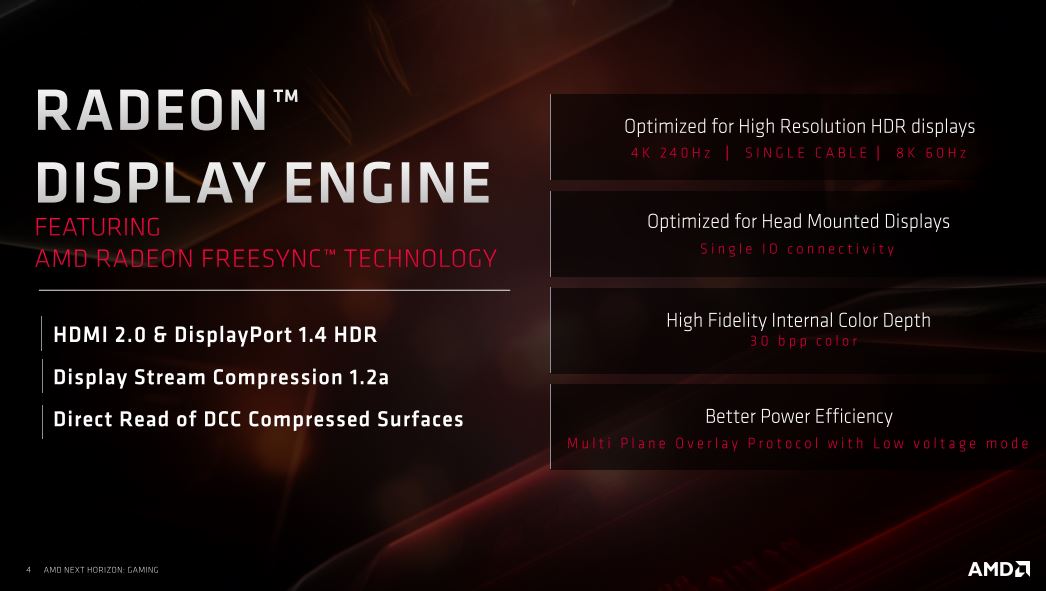

Aside from that, the new Radeon Display Engine also features full support of HDMI 2.0 and DisplayPort 1.4 HDR monitors. As such, the cards support both 4K at 240 Hz and 8K at 60 Hz with a full color palette with maximum depth. NAVI also supports VP9, H.264 MPEG-4 and H.265 HEVC video codecs, which will be an advantage for the many streamers on various platforms.
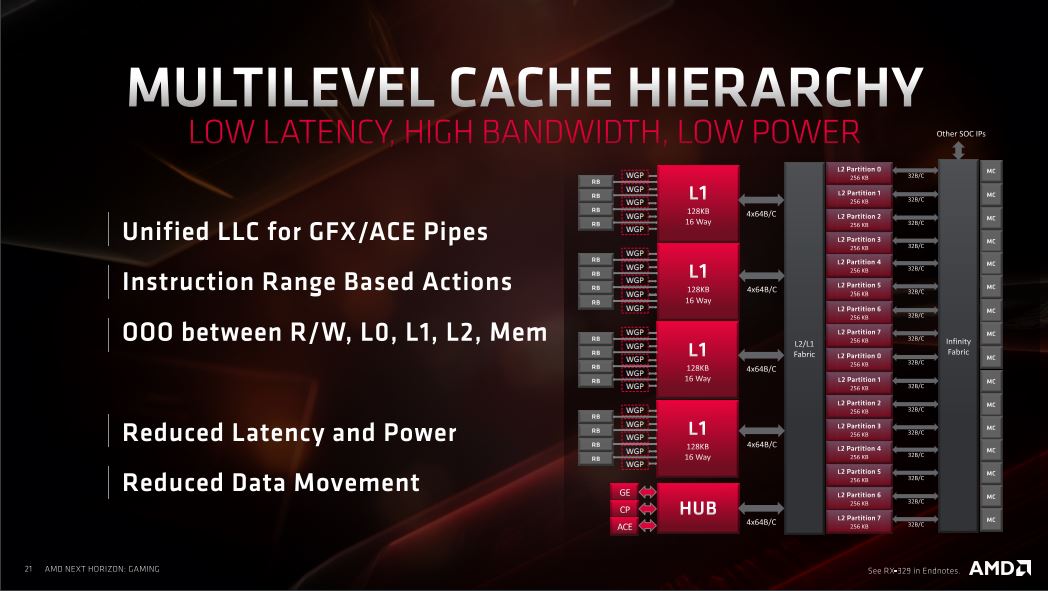
NAVI features a multilevel cache which means that the latency between pipelines is reduced significantly. One can say that the different pipelines have received their own L1 cache, which is connected to a large freeway that connects the many L2 cache partitions that are also present on the graphics card’s PCB. Finally, everything is connected to the rest of the graphics card via AMD’s patented Infinity Fabric which connects all of the components on the graphics card.
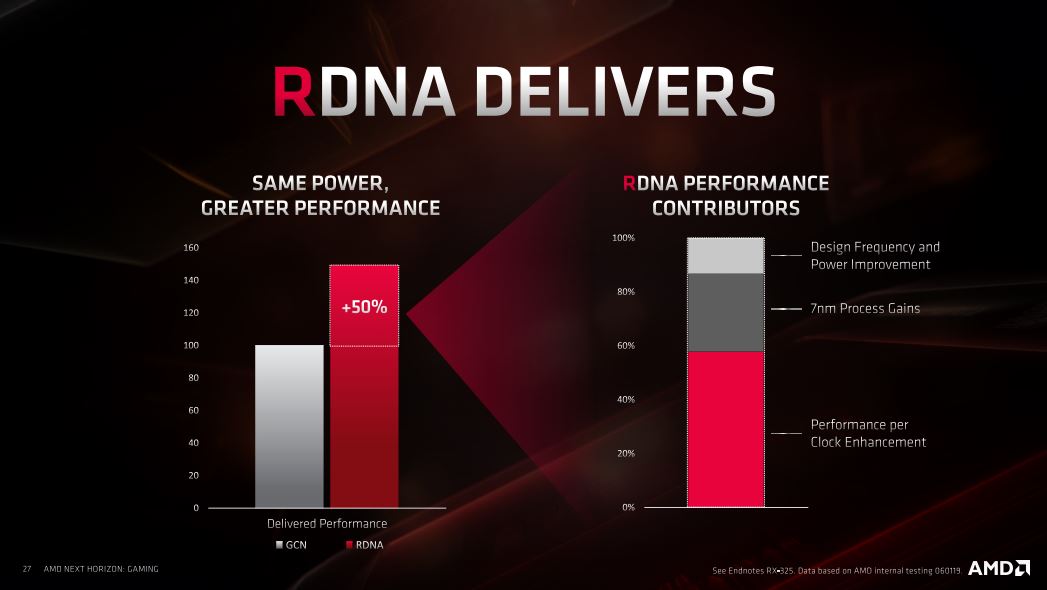
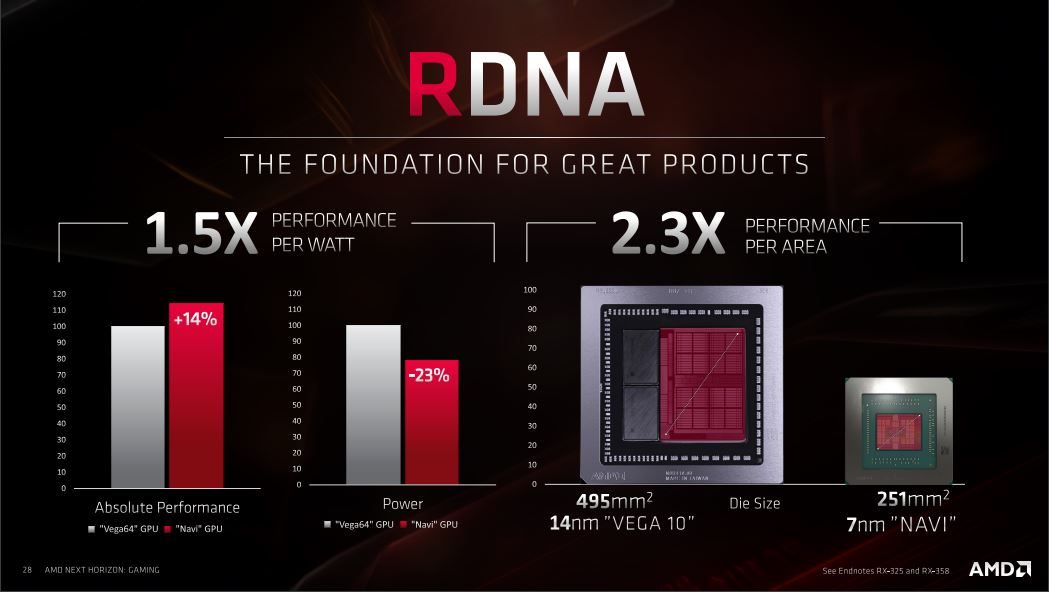
Overall, the RDNA architecture of NAVI brings great improvements at the same level of power consumption that we saw with the GCN architecture. This in part comes from the improvements to the design and power optimization. The switch to 7 nm silicone also does a great deal since this is a physical reduction of the size of the chip. In fact, we see a 50% power optimization when we look at performance per watt and a whopping 130% performance gain in relation to the size of the chip.

The RDNA architecture also brings some software technologies to the table that should improve the user experience when gaming. One of these is the Radeon Image Sharpening, which simply put increases the sharpness of the image.
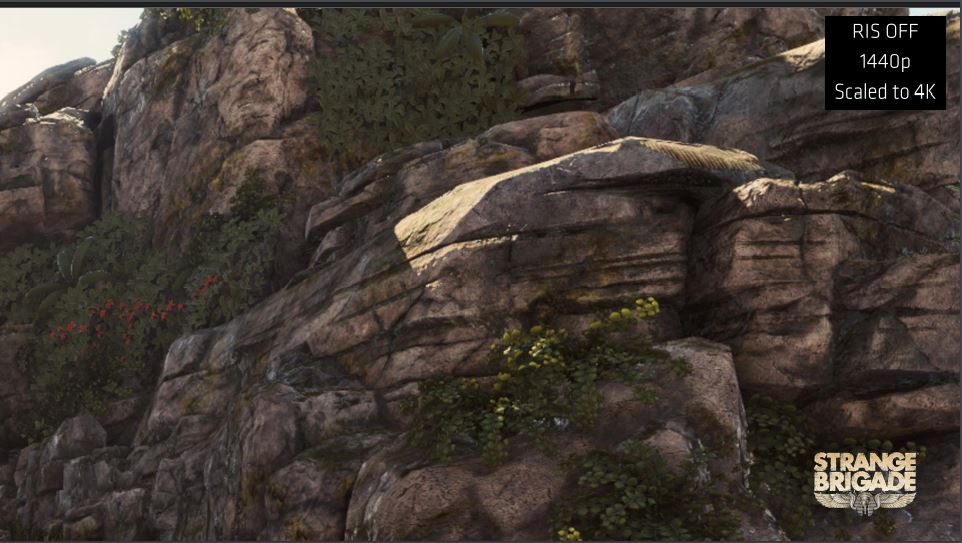
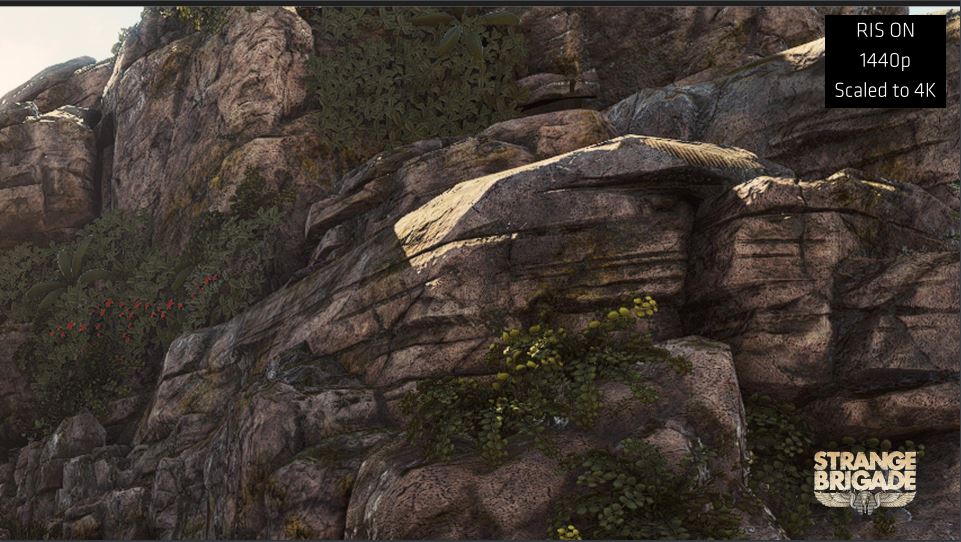


Comparison between Radeon Image Sharpening turned on and off taken from the game Strange Brigade.
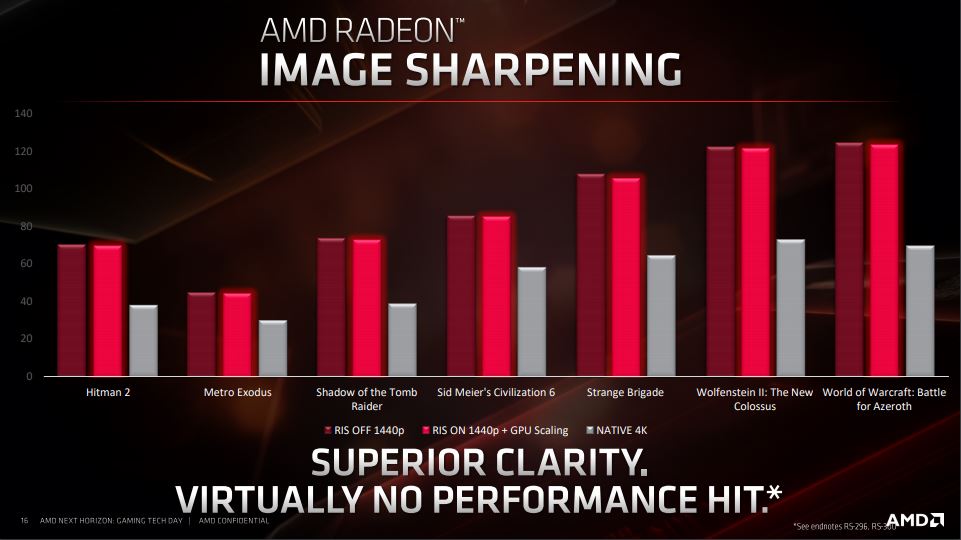
As usual the big question, when it comes to image optimization, is what it will demand in terms of performance. However, the Radeon Image Sharpening technology is pretty much seamless in terms of performance requirement even though it improves the sharpness in games, thus increasing the level of detail.

The Radeon Software also provides AMD Fidelity FX, which is also known as CAS (Contrast Adaptive Sharpening). This technology isn’t exactly new and it was also present with the VEGA cards. However, everything counts when it comes to having the sharpest image. As long as it is performance friendly then it’s worth including.
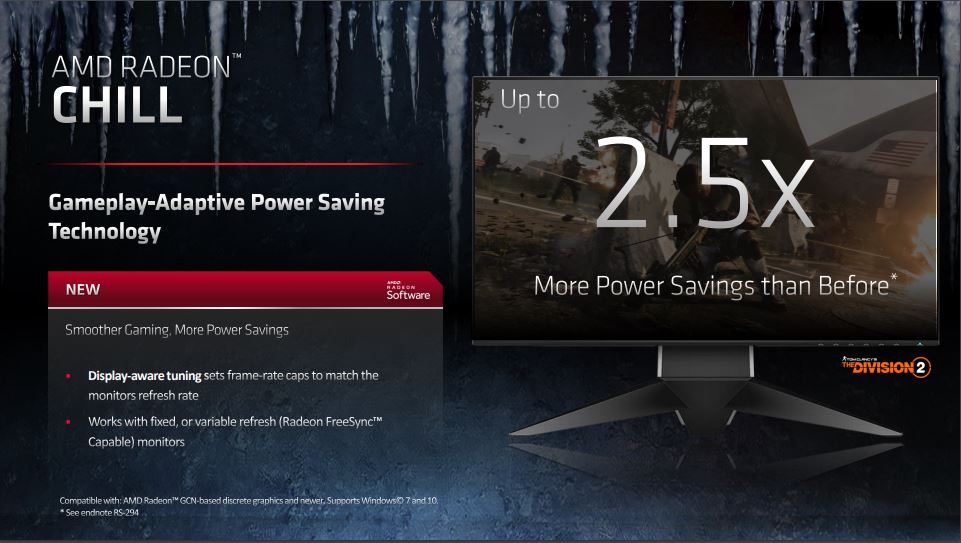
Radeon Chill is also still to be found, and this is all about calculating the performance need dynamically, and reducing the number of frames sent to the monitor when the need is not there for a high frame rate. This contributes to the power optimization aspect and it works with variable refresh rates of FreeSync monitors.
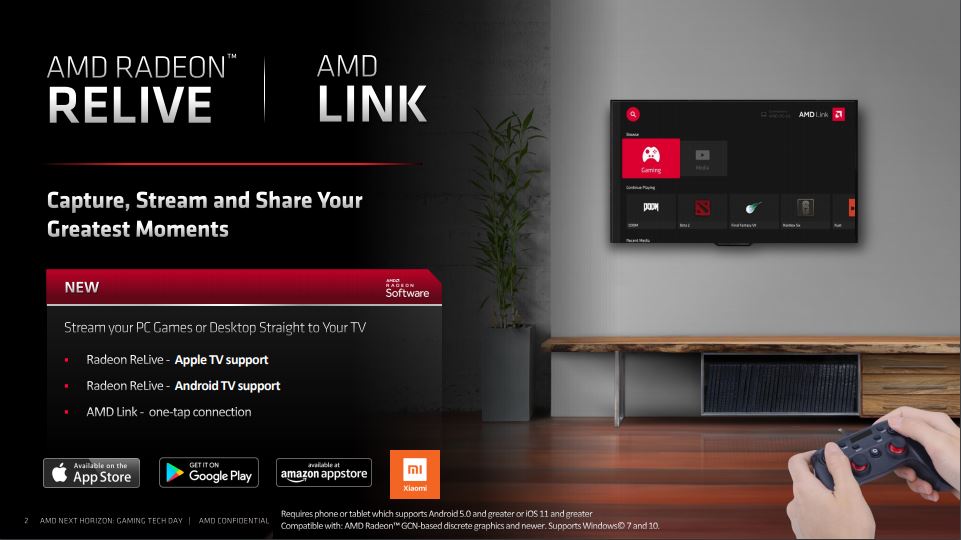
Radeon Relive is a capture/streaming software that allows you to connect to your TV so that you can play your PC games directly on your living room altar via mouse and keyboard, or a controller. It’s essentially an equivalent to other similar software such as Steam on NVIDIA Shield that lets you stream your Steam games on your TV.

So, all in all, we are seeing some new technology at play, which brings better gaming experiences via image optimization and lower latency as well as significant power consumption optimizations.
Latest graphics card
-
20 Margraphics card
-
13 Jangraphics card
ASRock B580 Steel Legend
-
07 Jangraphics card
ASUS showcases new AMD RX 9700 graphics cards
-
07 Jangraphics card
ASUS ready with large selection of RTX 50 graphics
-
07 Jangraphics card
Nvidia Reflex 2 reduces gaming latency
-
07 Jangraphics card
Nvidia launches DLSS 4 with the new RTX 50 series
-
07 Jangraphics card
Nvidia RTX 50 series is ready
-
07 Jangraphics card
Nvidia launches RTX 5090 at CES
Most read graphics card
Latest graphics card
-
20 Margraphics card
ASRock RX 9070 Steel Legend
-
13 Jangraphics card
ASRock B580 Steel Legend
-
07 Jangraphics card
ASUS showcases new AMD RX 9700 graphics cards
-
07 Jangraphics card
ASUS ready with large selection of RTX 50 graphics
-
07 Jangraphics card
Nvidia Reflex 2 reduces gaming latency
-
07 Jangraphics card
Nvidia launches DLSS 4 with the new RTX 50 series
-
07 Jangraphics card
Nvidia RTX 50 series is ready
-
07 Jangraphics card
Nvidia launches RTX 5090 at CES






